Mortgage rates, an essential factor in the home buying process, often sway the decisions of potential homeowners. Forecasting these rates involves examining various economic indicators and market trends to provide insights into potential future fluctuations.
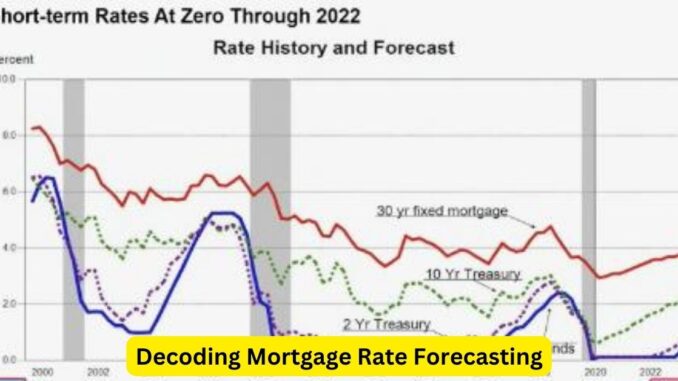
Historically, mortgage rates have displayed sensitivity to broader economic conditions, particularly movements in the bond market. The benchmark for mortgage rates is often tied to the yield on the 10-year Treasury note. When bond yields rise due to factors like economic growth or inflation expectations, mortgage rates tend to follow suit.
The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy also plays a pivotal role. The Fed’s decisions on interest rates directly influence short-term borrowing costs for financial institutions. However, while the Fed’s actions don’t directly control mortgage rates, they can indirectly impact them, particularly in the short term.
Economic indicators such as employment data, inflation rates, GDP growth, and consumer spending serve as key metrics in forecasting mortgage rate trends. For instance, strong economic growth might signal higher inflation, prompting an increase in mortgage rates to hedge against inflationary pressures.
Geopolitical events and global economic trends also contribute to rate fluctuations. International factors, such as trade policies, global financial crises, or geopolitical tensions, can influence investor behavior and impact bond markets, subsequently affecting mortgage rates.
Predicting future mortgage rates involves a combination of analyzing these economic indicators, market sentiment, and expert insights. Financial institutions, economists, and analysts use sophisticated models and historical data to make forecasts, but it’s important to note that these predictions are subject to change based on evolving market conditions.
Recent trends have shown a gradual rise in mortgage rates after a period of historic lows. Factors like economic recovery from the pandemic-induced slowdown, rising inflation concerns, and the Fed’s adjustments to its monetary policy stance have contributed to this upward trajectory.
However, the pace and extent of rate increases remain uncertain. External factors like the course of the pandemic, geopolitical tensions, and shifts in global economic dynamics can influence the direction of rates. Anticipating how these variables will evolve and interact is a complex task in mortgage rate forecasting.
For prospective homebuyers, staying informed about these forecasts can be beneficial in timing their purchase decisions. Locking in a mortgage rate during a period of lower rates can lead to substantial long-term savings on interest payments.
Ultimately, while forecasting mortgage rates involves analyzing a myriad of economic and market factors, it’s important to approach predictions with a degree of caution. Market conditions can change rapidly, and unforeseen events can disrupt anticipated trends. Monitoring economic indicators and seeking guidance from financial experts can help individuals make informed decisions amidst the dynamic landscape of mortgage rate forecasting.

Leave a Reply